GSFrag
General information. The GSFRAG program allows one to calculate the occurrence numbers of certain special fragments on k=2,...,10 vertices in a molecular graph G that can be used as molecular descriptors in quantitative structure-property/activity studies.
Description of fragments. We consider molecular fragments consisting of one or more disconnected components. Each component is a path (of length 9 or less), a cycle (on 10 or less vertices), or a path (cycle) with a number of attached chains of unit length. We call such fragments “primary”. Each fragment has unique name which is formed by the following rule. We denote a path of length n by symbol “pn” and a cycle on m vertices by “cm”. We also label each atom of the path (cycle) by the Latin capital A, B, etc. If the path (cycle) has some attached chains, labels of the corresponding atoms are listed next. In this manner one may get the name of each component of a given fragment. The name of a complete basic fragment is then formed by concatenating the names of each individual component (primary fragment). This naming scheme is illustrated by the picture below.
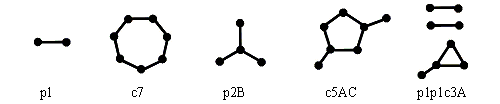
Applications. Using the GSFRAG program many numerical experiments were done. It was established that occurrence numbers of considered fragments in a graph produce a unique code of chemical structure for many large classes of compounds. Model QSPR/QSAR equations constructed from these descriptors usually provide good statistical characteristics and high predictive ability.
References
- Skvortsova M.I., Baskin I.I., Skvortsov L.A., Palyulin V.A., Zefirov N.S., Stankevich I.V. Chemical graphs and their basis invariants. J. Mol. Structure (Theochem). 1999. 466 (1-3) 211-217.
- Skvortsova M.I., Fedyaev K.S., Baskin I.I., Palyulin V.A., Zefirov N.S. A New Technique for Coding Chemical Structures Based on Basis Fragments. Doklady Chemistry. 2002. 382 (4-6) 33-36. Translated from: Doklady Akademii Nauk (Russ.), 2002. 382 (5) 645-648.
GSFragl
General information. The GSFRAG-L program is an extension of the program GSFRAG. It allows one to calculate the occurrence numbers of special molecular fragments on k=2,...,7 vertices containing one labeled vertex. Occurrence numbers can be used as molecular descriptors in quantitative structure-property/activity studies in order to describe the effect of hetero atoms.
Description of fragments. Let us consider unlabeled molecular fragments of the same structure as in the GSFRAG program. Each fragment consists of one or more disconnected components (primary fragments): paths of length n, 1<=n<=6 (denoted by symbol "pn"), cycles on m vertices, 3<=m<=7 (denoted by "cm"), or paths (cycles) with a number of attached chains of unit length (we label each atom of the path/cycle by the Latin capital A, B, etc. and list labels of atoms corresponding to attached chains after the path/cycle name). A name of the whole fragment is formed by concatenating names of each individual component. In the GSFRAG program such fragments are called "basic". In the next step we mark one of the atoms in the basic fragment by one of the following labels: C, N, O, S, Cl, Br, I, F. So we get a molecular fragment with one labeled vertex. Atoms in the unlabeled fragment are numbered sequentially (in paths/cycles with attached chains atoms of the path/cycle are numbered first). A name of the labeled fragment is formed by adding to the unlabeled fragment name (after a dash) the number of labeled atom and the label name. Examples of molecular fragments with a labeled vertex are given in the picture below.
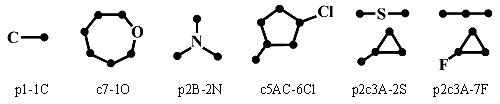
Applications. Molecular fragments of this type provide good correlations between properties and chemical structure for many classes of compounds. Corresponding molecular descriptors are expected to be widely used in QSAR/QSPR studies.
References
- Skvortsova M.I., Baskin I.I., Skvortsov L.A., Palyulin V.A., Zefirov N.S., Stankevich I.V. Chemical graphs and their basis invariants. J. Mol. Structure (Theochem). 1999. 466 (1-3) 211-217.
- Skvortsova M.I., Fedyaev K.S., Baskin I.I., Palyulin V.A., Zefirov N.S. A New Technique for Coding Chemical Structures Based on Basis Fragments. Doklady Chemistry. 2002. 382 (4-6) 33-36. Translated from: Doklady Akademii Nauk (Russ.), 2002. 382 (5) 645-648.